Since 2000, with the enactment of Legislative Decree No. 66, work involving exposure to hardwood dust has in fact been included among the work with a carcinogenic risk for humans, as exposure to these substances can cause the onset of various diseases if inhaled through the air.

Wood dust can be hard or soft. Hardwood dust from certain types of wood is considered harmful and can cause cancerous diseases of epithelial origin. These diseases, which are rare overall, occur more frequently (approximately 5-10 times) in wood workers. The estimated latency period is 20-40 years, with an age of onset between 55 and 70 years. In addition to malignant neoplasms, other diseases such as dry coughs, chronic coughs, recurrent colds, eye and nose irritation, and asthma, all associated with wood work, are recognised.
The professions at risk of exposure to hardwood dust are mainly related to the timber production and processing sector, particularly in processes such as debarking, sawing, sanding, planing, profiling, sanding, dusting and assembly. This risk involves carpenters, furniture makers, forestry workers and woodworkers. The production of furniture, fixtures and other wood products often involves exposure to hazardous chemical agents such as dust, aerosols and vapours, with the main risk associated with inhalation. Chemical agents can arise either from direct use (paints and solvents) or from the work process (dust production during sanding, sanding, etc.).

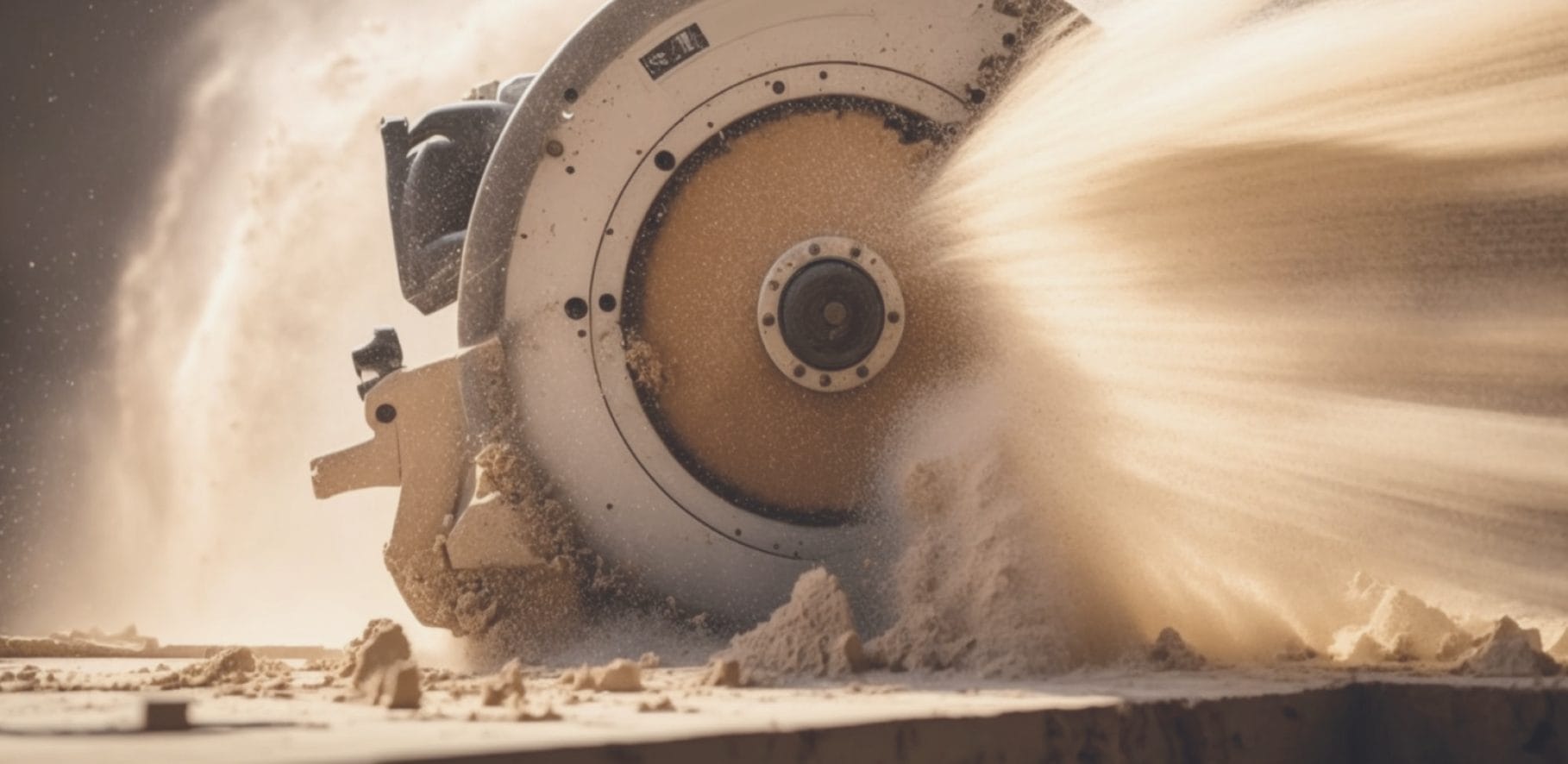
Wood dust, with a diameter of between 10 and 30 thousandths of a millimetre in machining operations, poses a significant risk. Their extreme thinness facilitates airborne dispersion, inhalation and penetration into exposed tissues. The carcinogenic hazard is associated with the inhalable fraction of airborne dust, and their microscopic size allows them to act at the cellular level, through mechanical, allergic and toxic mechanisms, endangering the body's overall health.
Exposure to wood dust can often also involve exposure to chemicals such as formaldehyde, which is commonly used in the carpentry industry for the production of various types of wood. This exposure can occur during the processing of plywood, laminated wood, chipboard and plywood, as well as in the production of furniture, furnishings, restoration and repair of wooden furniture and fixtures, and painting of wooden furniture and floors. There is also the possibility of exposure to asbestos, a fibre previously used in the wood and cork industry for the production of plywood and panels.
Cancer pathologies associated with hardwood dusts are recognised by INAIL as having a high probability of occupational origin in Group 6 of occupational cancers. These pathologies include tumours of the nasal cavities, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. Carpentries, which are increasingly integrated with wood end-users, have to deal not only with hardwood dust, but also with volatile organic substances generated by wood treatments.



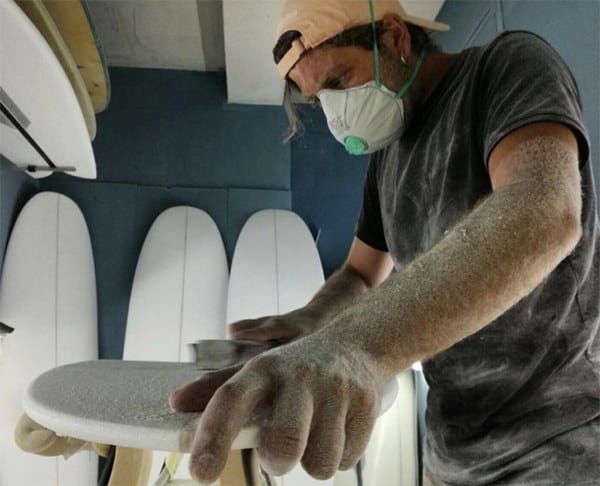
In order to mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement and comply with specific safety measures, such as the use of environmental prevention systems (e.g. vacuum systems) and personal protective equipment (e.g. respiratory protective equipment).
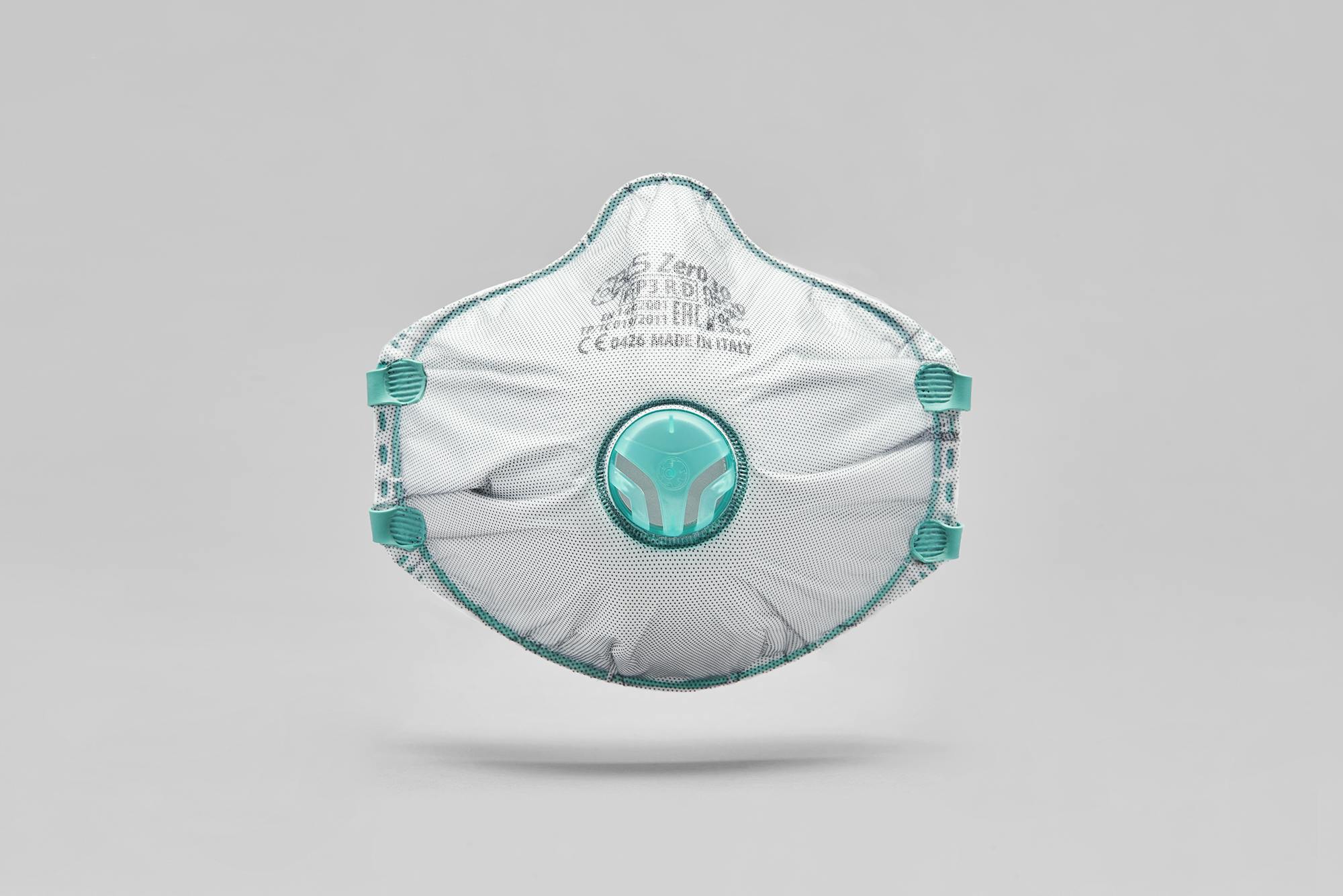
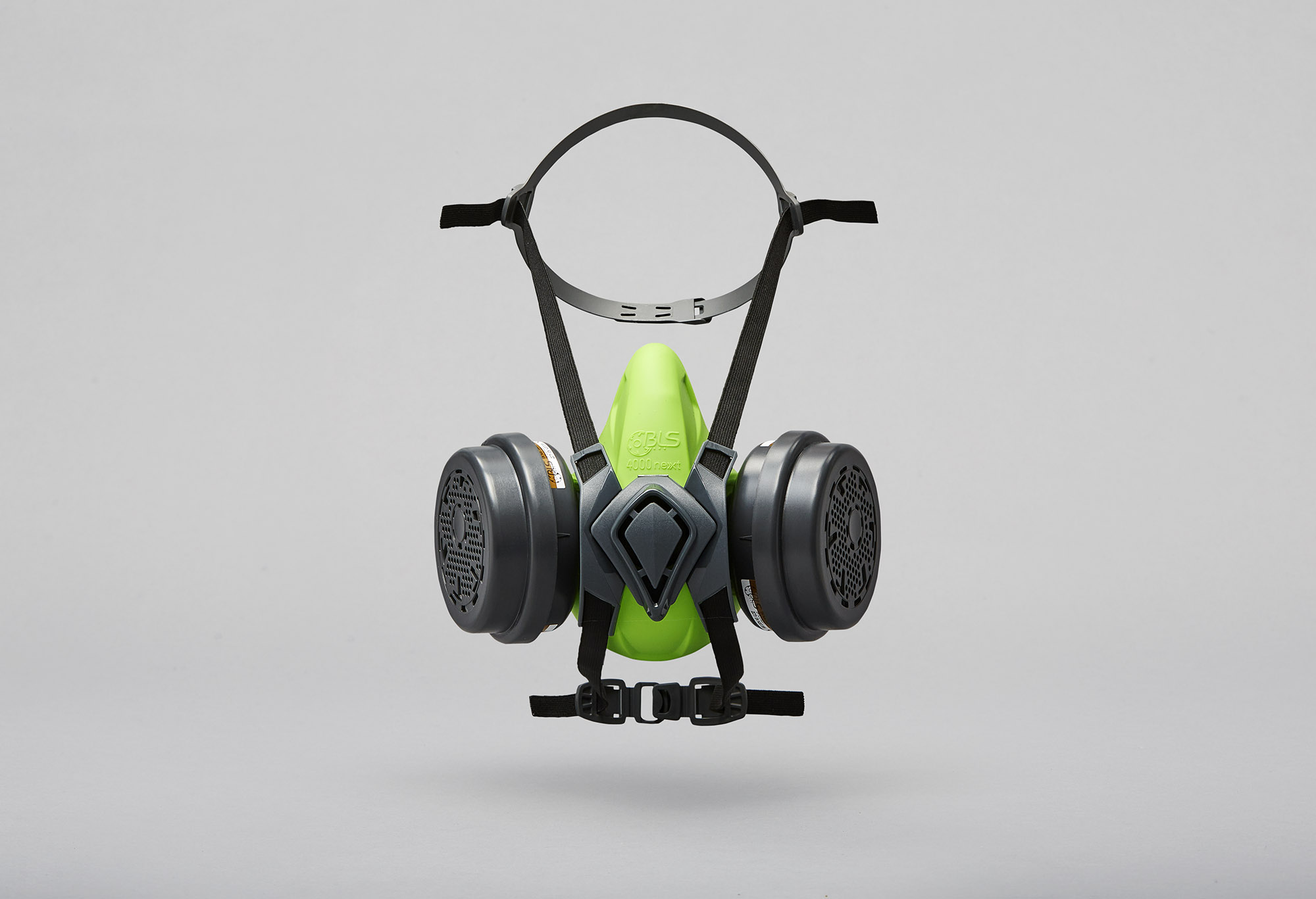
Filtering face masks with FFP2/FFP3 protection are required to protect against wood dust. However, we recommend the use of FFP3 filtering face masks with an efficiency of over 98%, together with protective systems against the inhalation of vapours and gases. These include type A and AX filters, which protect against organic gases and vapours respectively. These individual protection measures are in addition to collective systems such as forced ventilation and localised breathing.